In today's highly competitive business environment, companies are constantly seeking ways to maintain and enhance their competitive edge. One effective strategy is the use of holding companies.
Holding companies can play a pivotal role in building business competitiveness, covering various aspects such as their definition, advantages, strategic uses, financial benefits, governance, and real-world case studies.
In today's financial space, holding companies are similar to family offices, where investors of the family office can earn profit from their share of all the companies they own through the holding company.
At PIF Capital, we educate SME business owners and entrepreneurs on the perks of creating a holding company and how anyone can take advantage of it by joining our weekly IPO3 event happening every Tuesday from 9 am to 11 pm.
Key Takeaways
- Holding companies can provide significant tax benefits, which can enhance overall business profitability.
- They offer a robust mechanism for risk management by segregating liabilities among different subsidiaries.
- Holding companies can streamline operations, leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
- Strategically utilizing holding companies can facilitate market expansion and diversification of business portfolios.
- Effective governance and centralized decision-making in holding companies can lead to better stakeholder management and corporate governance.
Understanding the Role of Holding Companies
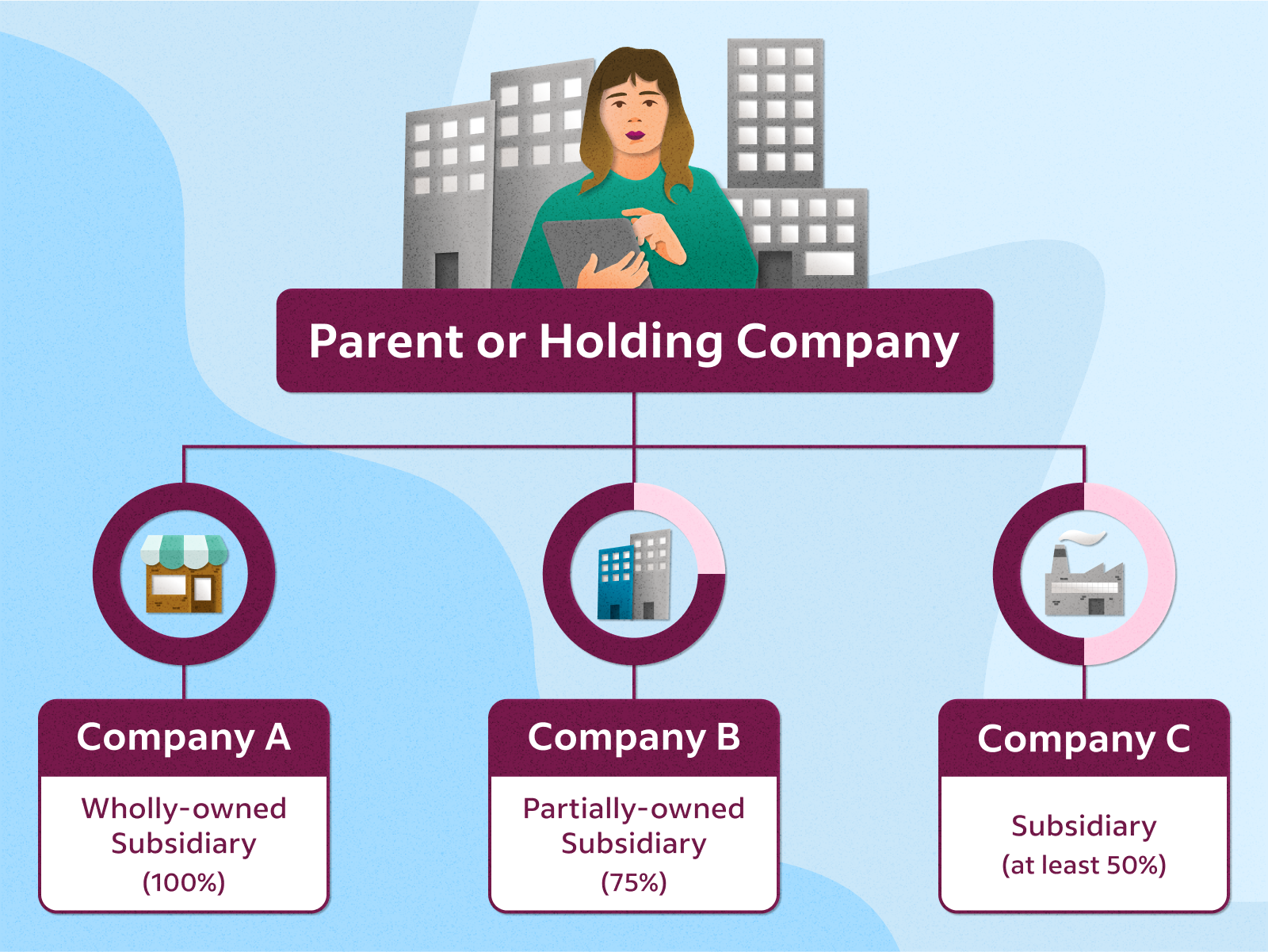
A holding company is a parent company—usually a corporation or LLC—that is created to buy and control the ownership interests of other companies. This structure allows the holding company to manage and oversee its subsidiaries without being involved in their day-to-day operations. The primary purpose of a holding company is to own assets, such as stocks, real estate, or intellectual property, and to manage the risk associated with these assets.
Types of Holding Companies
There are several types of holding companies, each serving different strategic purposes:
- Pure Holding Companies: These companies exist solely to own shares of other companies.
- Mixed Holding Companies: These companies not only hold shares but also engage in their own business operations.
- Immediate Holding Companies: These are subsidiaries of larger holding companies but also hold their own subsidiaries.
- Intermediate Holding Companies: These companies are both a subsidiary and a parent company within a larger corporate structure.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Operating a holding company involves navigating various legal and regulatory frameworks. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal pitfalls and ensure smooth operations. Key considerations include:
- Corporate Governance: Establishing a robust governance structure to oversee subsidiaries.
- Taxation: Understanding the tax implications and benefits of holding company structures.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to industry-specific regulations and reporting requirements.
Effective management of legal and regulatory aspects can significantly enhance the competitiveness of a holding company. By understanding the role and structure of holding companies, businesses can strategically position themselves for growth and risk management.
Advantages of Holding Companies

Tax Benefits
Holding companies can offer significant tax advantages. By strategically locating subsidiaries in jurisdictions with favorable tax laws, businesses can minimize their overall tax burden. This structure allows for the efficient allocation of profits and losses across the group, optimizing tax obligations.
Risk Management
A holding company structure helps in isolating risks. If one subsidiary faces financial difficulties, the holding company and other subsidiaries remain protected. This separation ensures that the failure of one entity does not jeopardize the entire business group.
Operational Efficiency
Holding companies can streamline operations by centralizing key functions such as finance, HR, and IT. This centralization leads to cost savings and improved efficiency, allowing subsidiaries to focus on their core activities.
The holding company holds the majority of the stocks of the subsidiaries. This also protects the interest of everyone since it disables any of the major subsidiaries from making unilateral decisions that could affect the entire group.
Strategic Use of Holding Companies
Holding companies can be instrumental in entering new markets. By acquiring or establishing subsidiaries in different regions, a holding company can quickly gain a foothold without the need for extensive groundwork. This approach allows for leveraging the existing market presence and customer loyalty of the acquired entities.
Diversification is another strategic advantage. Holding companies can invest in various industries, spreading risk and capitalizing on multiple growth opportunities. This not only stabilizes financial performance but also opens up new revenue streams.
Subsidiaries under a holding company can benefit from shared resources and expertise. This synergy can lead to improved innovation and operational efficiency. Additionally, holding companies can streamline decision-making processes, ensuring that subsidiaries align with the overall strategic goals.
Holding companies benefit through financial performance, dividends, and growth opportunities provided by their subsidiaries, leveraging their strategic position to enhance market competitiveness.
Financial Benefits of Holding Companies
At PIF Capital, we often share the financial benefits of holding companies so they can continuously expand their business without having to worry about the day-to-day troubles.
Access to Capital
Holding companies often have enhanced access to capital due to their diversified portfolio and consolidated financial strength. This allows them to secure funding at more favorable terms compared to individual subsidiaries. Additionally, they can leverage their assets to raise capital more efficiently.
Improved Creditworthiness
The consolidated financial statements of holding companies typically reflect a stronger financial position, which can lead to improved credit ratings. This, in turn, enables them to obtain loans and other forms of credit at lower interest rates, further enhancing their financial flexibility.
Cost Savings
Holding companies can achieve significant cost savings through economies of scale. By centralizing functions such as procurement, marketing, and administration, they can reduce operational costs. Moreover, they can negotiate better terms with suppliers due to their higher market share, leading to further savings.
Holding companies offer flexibility in investment strategies, allowing them to diversify their portfolio by holding interests in various companies. This diversification can lead to more stable and predictable financial performance.
Governance and Control in Holding Companies
Governance and control are pivotal aspects of holding companies, ensuring that the organization operates efficiently and aligns with its strategic goals. Centralized decision-making is a hallmark of holding companies, allowing the parent entity to directly control one or more subsidiaries. This centralized approach facilitates streamlined decision-making processes and ensures that all subsidiaries adhere to the overarching corporate strategy.
Centralized Decision-Making
Centralized decision-making in holding companies enables the parent company to exercise oversight and strategic control over its subsidiaries. This structure helps in maintaining uniformity in operations and strategic alignment across the entire organization.
Corporate Governance Structures
Effective corporate governance structures are essential for holding companies to function smoothly. These structures define the roles and responsibilities of the board of directors, management, and other stakeholders, ensuring accountability and transparency in operations.
Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management is crucial in holding companies, as it involves balancing the interests of various parties, including shareholders, employees, and customers. Proper stakeholder management ensures that the company maintains a positive reputation and fosters long-term relationships with key stakeholders.
Governance and control mechanisms in holding companies are designed to ensure that the organization operates efficiently and aligns with its strategic goals.
Case Studies of Successful Holding Companies
Global conglomerates often serve as prime examples of successful holding companies. These entities manage a diverse portfolio of businesses across various industries, showcasing their ability to leverage subsidiaries for market dominance.

For instance, Berkshire Hathaway, led by Warren Buffett, owns a multitude of companies ranging from insurance to retail, demonstrating the strategic advantage of diversification.
Family-owned holding companies also illustrate the potential for long-term success. These companies often benefit from a centralized decision-making process and a strong sense of corporate governance. The Mars family, for example, has maintained control over Mars, Incorporated, ensuring consistent growth and stability through generations.

In the tech industry, holding companies have been instrumental in fostering innovation and expansion. Alphabet Inc., the parent company of Google, exemplifies how a holding company structure can facilitate the growth of various subsidiaries, each focusing on different technological advancements. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risk by diversifying investments.
Holding companies, whether global conglomerates, family-owned, or tech-focused, provide valuable insights into how strategic management and diversification can lead to sustained business competitiveness.
Challenges and Risks Associated with Holding Companies
Regulatory Compliance: Holding companies must navigate a complex web of regulations across different jurisdictions. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties and legal issues. The need for separate subsidiary records adds to the complexity, making transparency a challenge.
Management Complexity: The structure of holding companies often leads to intricate management challenges. Coordinating activities across multiple subsidiaries requires robust systems and processes. This complexity can hinder decision-making and operational efficiency.
Potential Conflicts of Interest: Conflicts of interest can arise when the interests of the holding company diverge from those of its subsidiaries. This can lead to strategic misalignments and operational inefficiencies. It is crucial to establish clear governance structures to mitigate these risks.
Holding companies have disadvantages such as complex structure, increased risk due to the need for separate subsidiary records, and transparency challenges.
Have You Set Up Your Holding Company?
By leveraging strategic alliances, enhancing customer experience, and continuously analyzing market dynamics, businesses can create a sustainable competitive edge.
While this article provides a comprehensive overview, the journey to competitiveness is ongoing and requires constant adaptation and innovation. Don't hesitate to seek professional guidance to navigate this complex landscape and ensure your business remains at the forefront of the industry.